Portal frame load cases
The portal frame builder generates a number of primary load cases that represent the dead loads, live loads and wind loads for each of the orthogonal building directions.
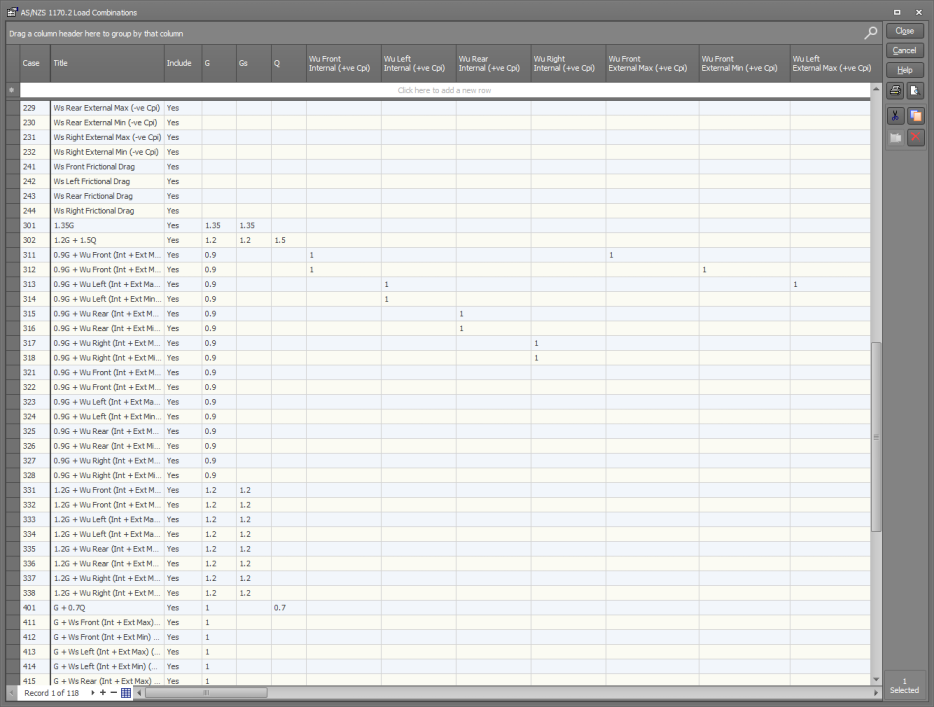
For AS/NZS1170.2
Wind load cases 101 to 112 are for the ultimate internal and external wind pressures that apply to the positive ultimate Cp,i coefficient, followed by load cases 121 to 132 that apply to the negative ultimate Cp,i coefficient, followed by load cases 141 to 144 for the ultimate frictional drag forces. They are followed by a similar set of load cases for the serviceability limit state.
Note that the external wind load cases are affected by the Cp,i internal pressure coefficients because they affect the Kc,e factors which are dependent on whether or not wind pressures are acting on a combination of surfaces.
For IS875
Wind load cases 4 to 7 are for the ultimate limit state and represent an internal pressure coefficient of 1.0. Note that these are factored in the combination load cases to represent the actual internal pressure coefficients. Load cases 8 to 11 are also for the ultimate limit state and are based on the actual external pressure coefficients. They are followed by a further four wind load cases that represent the ultimate frictional drag forces.
The serviceability load cases are specified as combination load cases that factor the ultimate load cases by (Vzs/Vzu)2, where Vzs and Vzu are the design wind speeds for the serviceability and ultimate limit states respectively.
For each wind code, combination load cases are also generated to take into account numerous combinations of the dead loads, live loads and wind loads for the ultimate and serviceability limit states.
You can add extra combination load cases to this table, however it is sometimes easier to do this in the main SPACE GASS combination load cases datasheet once the model has been generated.