Area loads
One-way or two-way area loads can be generated by specifying a pressure that is applied to a roof or a floor or any other set of members that can form closed or open polygons. The pressure loads are converted to member distributed forces calculated from the contributing area of each member. You can select many members that form multiple open or closed areas and the area loading tool will process them all at once.
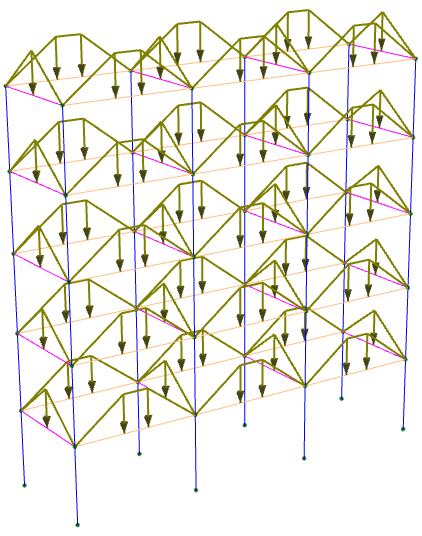
Two-way loads require closed areas formed by three or more perimeter members and the generated member loads are based on the load surface spanning in two directions, generally resulting in a mixture of uniform, triangular and trapezoidal loads.
One-way loads don't require closed areas and the generated loads are based on the load surface spanning in just one direction, resulting in uniformly distributed loads if the supporting members are parallel, or trapezoidal if the supporting members are not parallel.
After selecting the desired members to be loaded, right-click and then select "Loads" => "Generate Area Loads" from the popup menu that appears.
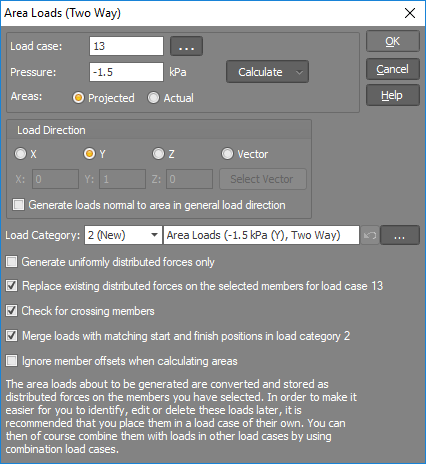
The "Generate" button opens the wind calculator that can be used to calculate a wind pressure based on various wind code dependent parameters such as site location, region, wind direction, return period, height, terrain categories, shielding, topography and pressure coefficients. For more information refer to "Wind Calculator".
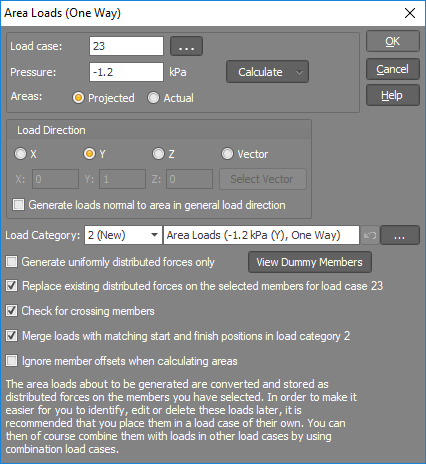
For one-way area loads, if you click the "View Dummy Members" button in the one-way area loading form shown below, you can visually see the dummy members that effectively "close" the open polygons on which the one-way loads are based. Of course, the "dummy" members don't exist and don't attract any load.
"Projected" areas results in the loads being based on the projected areas normal to the load direction, whereas "Actual" areas cause the generated loads to be based on the actual areas regardless of the load direction.
The load direction can be parallel to one of the global axes or along any vector that you specify. You can select the load direction vector graphically by clicking the "Select Vector" button.
The "Load category" field lets you specify which load category the generated loads will go into. For more information refer to "Load categories".
If the "Generate loads normal to area in general load direction" option is ticked then the pressure is applied in the general load direction that you have specified, but normal to each polygon. This is handy if you have a pitched roof and you want to apply a generally vertical wind load that is normal to the roof on both sides of the ridge.
The "Generate uniformly distributed forces only" option forces the pressure applied to a polygon to be applied uniformly to each member rather than as triangular or trapezoidal loads.
The "Check for crossing members" option checks for members that cross over each other which could result in areas that overlap. This check should normally be left on.
If the area loader generates loads on members that already contain loads in the same load case or if it generates multiple overlapping loads on the same member then the "Merge loads with matching start and finish positions" option will try to merge the loads rather than having two sets of loads with different sub-load numbers. This makes it easier to see the loads when they are viewed graphically. If this option is turned off then when identical loads are generated on a single member it might be difficult to differentiate between them when they are viewed graphically.
The "Ignore member offsets when calculating areas" option treats the members as if they have no offsets and could result in slightly inaccurate results if the member offsets affect the shape or size of the area. It should only be ticked if the area loader is unable to find the desired areas due to member offsets.